Circuit Model
The Zero-Knowledge circuit is the mathematical core that enforces the rules of verification without revealing secrets.
Concept
Deeproof uses a circuit written in Circom. The circuit's job is to answer the question:
"Does this user know a valid UserID and Trapdoor that hash to this Commitment, and is their KYC level sufficient?"
...without revealing the UserID or the Trapdoor.
Inputs
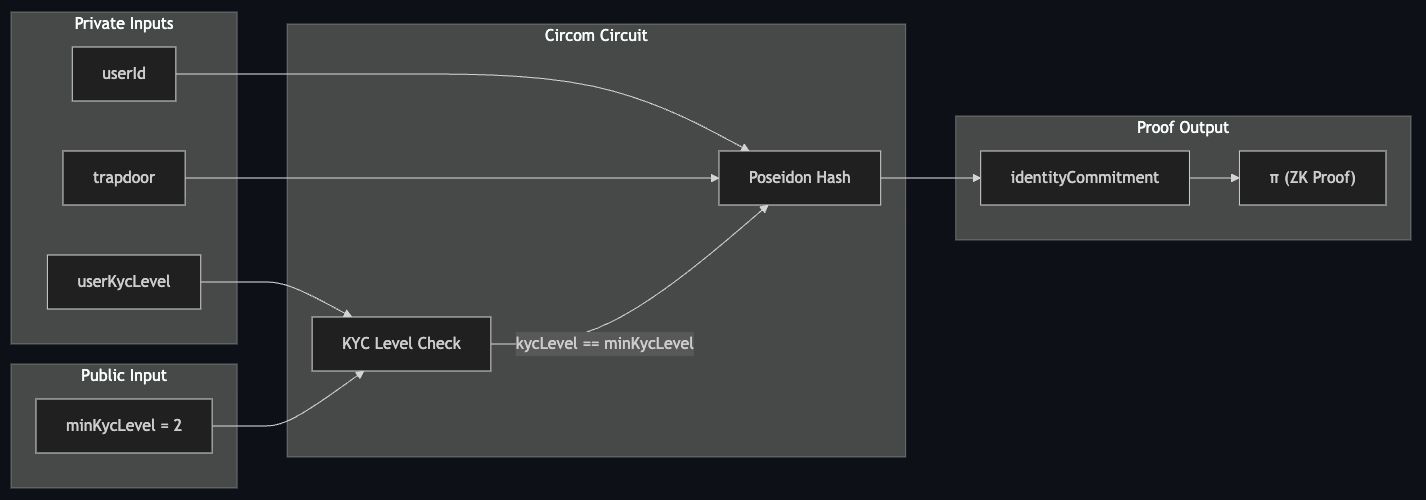
The circuit takes two types of inputs:
1. Private Inputs (Secret)
These values are known only to the user (prover) inside their browser. They are never revealed to the public or the contract.
userId: The unique identifier from the identity provider (e.g., Binance User ID).trapdoor: A random secret number generated by the user's extension. This acts as a password.userKycLevel: The actual KYC level retrieved from the provider.
2. Public Inputs (Visible)
These values are public and used by the smart contract to verify the proof.
minKycLevel: The minimum required KYC level (e.g., "2").identityCommitment: The resulting hash of the UserID and Trapdoor.
logic
The circuit performs the following checks:
- KYC Check: It asserts that
userKycLevelmatches (or is greater than)minKycLevel.- Logic:
userKycLevel === minKycLevelconstraint.
- Logic:
- Commitment Generation: It hashes the
userIdandtrapdoorusing the detailed Poseidon Hash algorithm.- Logic:
commitment = Poseidon(userId, trapdoor)
- Logic:
Output
The circuit outputs:
- The Proof: A cryptographic string proving the constraints are met.
- The Commitment: A public hash that represents the user's identity identity (like a fingerprint) but cannot be reversed to find the original ID.